FREE SHIPPING ON ORDERS OVER $350 (SOME EXCLUSIONS APPLY) | 877-4-SPRUCE
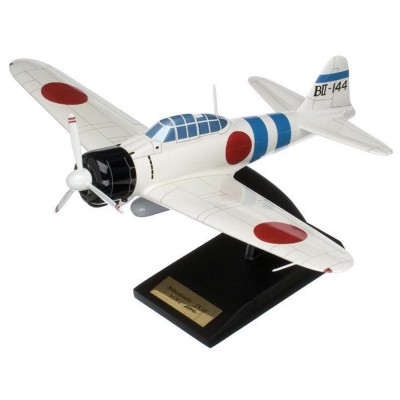
A6M5 Zero Model
$225.95/Each
Part# 13-10814
MFR Model# ESFN012
MFR Model# ESFN012
Overview
|
The A6M Zero is carrier-based fighter aircraft manufactured by Mitsubishi and was considered the best carrier-based fighter aircraft since the time it was produced. During 1940-1941, the pre-series A6M2 Zero became known, when the fighter was confirmed to have destroyed 266 aircraft in China. During Pearl Harbor, there were 420 Zeros in active service in the Pacific. In 1941, the Zero fighters were superior in many performance aspects to all Allied fighters in the Pacific and it quickly gained reputation. However, the Zero failed to achieve air superiority when suitable tactics and new aircraft were developed by the Allies. During World War II, the Zero destroyed at least 1,550 American aircraft. The A6M5 is an updated model of the A6M3 Model 22, with nonfolding wing tips and thinner skinning for faster diving speeds, plus an improved exhaust system which provides an increment of thrust. There are three subvariants of the A6M5, the A6M5a Model 52a, A6M5b Model 52b and A6M5c Model 52c. The A6M5 could travel at 540 km/h and can reach a height of 8,000 meters in nine minutes and 57 seconds. There were several Zero fighters which survived the war and were currently on display in Japan, China, United States and the UK, as well as the Auckland War Memorial Museum in New Zealand. |
WARNING: Cancer and Reproductive Harm - www.P65Warnings.ca.gov. |
Q&A
Please note, Aircraft Spruce's personnel are not certified aircraft mechanics and can only provide general support and ideas, which should not be relied upon or implemented in lieu of consulting an A&P or other qualified technician. Aircraft Spruce assumes no responsibility or liability for any issue or problem which may arise from any repair, modification or other work done from this knowledge base. Any product eligibility information provided here is based on general application guides and we recommend always referring to your specific aircraft parts manual, the parts manufacturer or consulting with a qualified mechanic.








 FREE Shipping
FREE Shipping